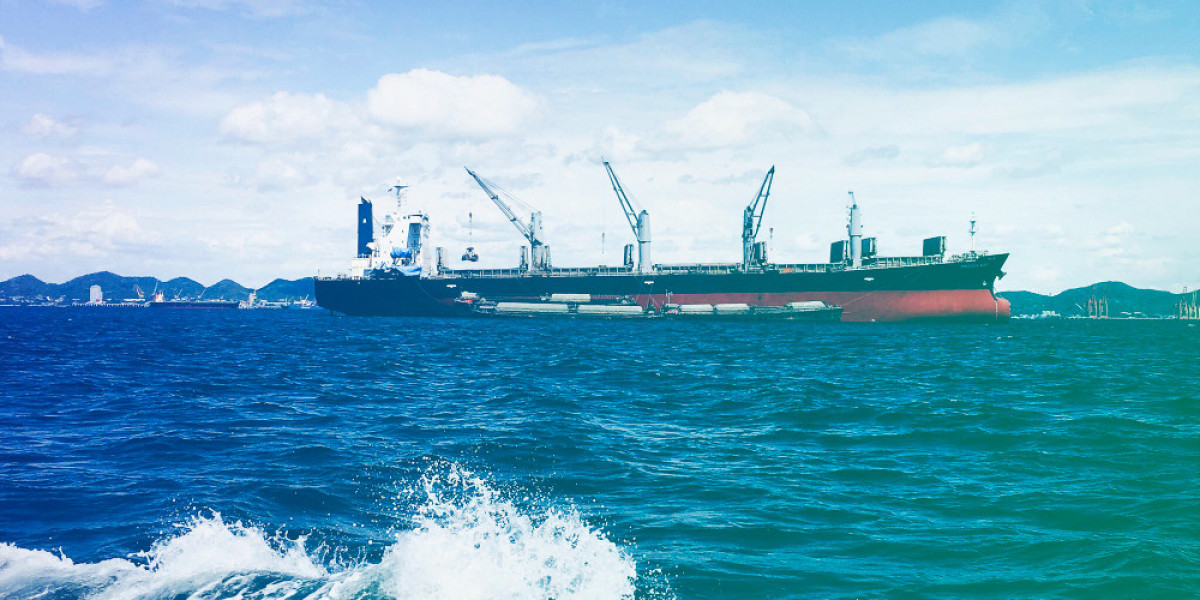
When it comes to transporting goods across the globe, sea freight remains one of the most reliable and cost-effective methods. The maritime industry handles approximately 90% of world trade, moving everything from raw materials to finished products across vast distances. Whether you’re an importer, exporter, or logistics manager, understanding the ins and outs of sea freight is essential to keeping your business competitive and cost-efficient.
What is Sea Freight?
Sea freight refers to the transportation of goods by ships over oceans and seas. It is one of the oldest and most established methods of transporting large quantities of goods internationally. This method is particularly advantageous for bulky, heavy, and non-perishable goods, making it the preferred option for many businesses, especially when cost-efficiency is key.
Unlike air freight, which is faster but typically more expensive, sea freight offers businesses the ability to move large volumes of goods at a fraction of the cost. However, the trade-off is longer delivery times, with shipments taking days or even weeks to reach their destination, depending on the distance.
Types of Sea Freight Services
Full Container Load (FCL): FCL refers to a sea freight service where a single shipper has enough goods to fill an entire container. This is a preferred option for large shipments as it provides direct, faster, and more secure transportation. It’s typically more cost-effective when you have enough cargo to fill the container.
Less than Container Load (LCL): LCL shipping is ideal for smaller shipments that don’t require an entire container. Instead of booking a whole container, multiple shipments from different businesses share the same container space. This method is more affordable for small businesses, but the trade-off is longer transit times due to additional loading and unloading.
Roll-on/Roll-off (RoRo): RoRo shipping is used primarily for vehicles and large equipment. This type of sea freight involves vehicles being driven directly onto the ship, which simplifies loading and unloading processes. It is often used for the transportation of cars, trucks, and other wheeled cargo.
Breakbulk: Breakbulk shipping refers to cargo that is too large or awkwardly shaped to fit into standard containers. These goods are typically transported individually and require special handling. This is commonly used for heavy machinery, industrial equipment, or large construction materials.
Advantages of Sea Freight
Cost-Effectiveness: Sea freight is the most cost-effective way to transport large quantities of goods over long distances. While the cost of shipping can vary based on factors like distance, fuel prices, and the size of the shipment, it is generally much cheaper than air freight or other forms of transportation.
Capacity: Ships can carry vast amounts of cargo compared to other modes of transportation, making sea freight an ideal solution for large shipments or bulk goods. This includes everything from raw materials like oil, coal, and grain to electronics, machinery, and consumer products.
Environmentally Friendly: Shipping by sea is considered more environmentally friendly than air freight due to its lower carbon footprint per ton-mile. Despite its size, the shipping industry produces less carbon dioxide compared to other modes of transportation, making it an attractive option for businesses aiming to reduce their environmental impact.
Global Reach: Sea freight connects businesses to almost every part of the world. Whether shipping between continents or moving goods from one island to another, the maritime shipping network is the most established and expansive global trade route.
Disadvantages of Sea Freight
Longer Transit Times: The most significant disadvantage of sea freight is the long transit time. Depending on the shipping route and distance, it can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks to transport goods via sea, which may not be ideal for time-sensitive shipments.
Weather and Delays: Sea freight is highly affected by weather conditions, including storms, high winds, and rough seas. While modern ships are equipped to handle adverse conditions, delays due to weather or port congestion can still occur.
Port Accessibility: Sea freight requires specific ports for loading and unloading. Not all regions have easy access to major shipping ports, which can increase costs or complicate logistics. Ports with limited capacity may also result in longer wait times.
How to Maximize Efficiency with Sea Freight
Plan Ahead for Long Transit Times: Sea freight can take a long time, so it’s important to plan shipments well in advance. By forecasting your inventory needs and shipping requirements, you can avoid rush orders and reduce the stress of tight delivery windows.
Optimize Container Space: Maximizing the use of container space is key to reducing overall costs. For example, if you’re shipping using FCL, make sure the container is fully packed to avoid paying for unused space. Similarly, if you’re using LCL, try to consolidate shipments to ensure you’re making the most of your shared container.
Choose the Right Shipping Partner: Selecting a reliable sea freight service provider is crucial. Look for providers with a track record of on-time deliveries, good customer support, and the ability to handle your specific shipping needs. Many companies offer specialized services for certain industries, so finding one that understands your product requirements can make a big difference.
Understand Shipping Terms: It’s important to be familiar with Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) when using sea freight. These terms define who is responsible for various costs and risks at different stages of the shipping process. Understanding whether you’re using FOB (Free On Board), CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), or another term can help you manage logistics costs effectively.
Track Shipments: Modern sea freight services often include tracking capabilities that allow you to monitor your shipments in real-time. Tracking tools provide peace of mind and allow you to stay updated on your goods' journey, helping you manage inventory levels and plan for their arrival.
The Future of Sea Freight
The sea freight industry is continuously evolving with advances in technology. One of the most promising trends is the development of smart shipping, where data and analytics are used to optimize routes, reduce fuel consumption, and improve safety. Additionally, environmental regulations are pushing the industry toward cleaner and more sustainable practices, with the development of eco-friendly ships and alternative fuel sources.
Conclusion
Sea freight remains a fundamental component of global trade, offering businesses an affordable and efficient way to transport goods worldwide. While there are challenges such as longer transit times and potential weather-related delays, the advantages far outweigh the drawbacks for many companies, especially those dealing with bulk or non-perishable goods.
By understanding the different types of sea freight, optimizing logistics strategies, and choosing the right partners, businesses can harness the power of sea freight to drive growth, reduce costs, and streamline supply chains in an increasingly connected world. As technology and sustainability continue to shape the future of the shipping industry, sea freight will undoubtedly remain a cornerstone of international trade for years to come.