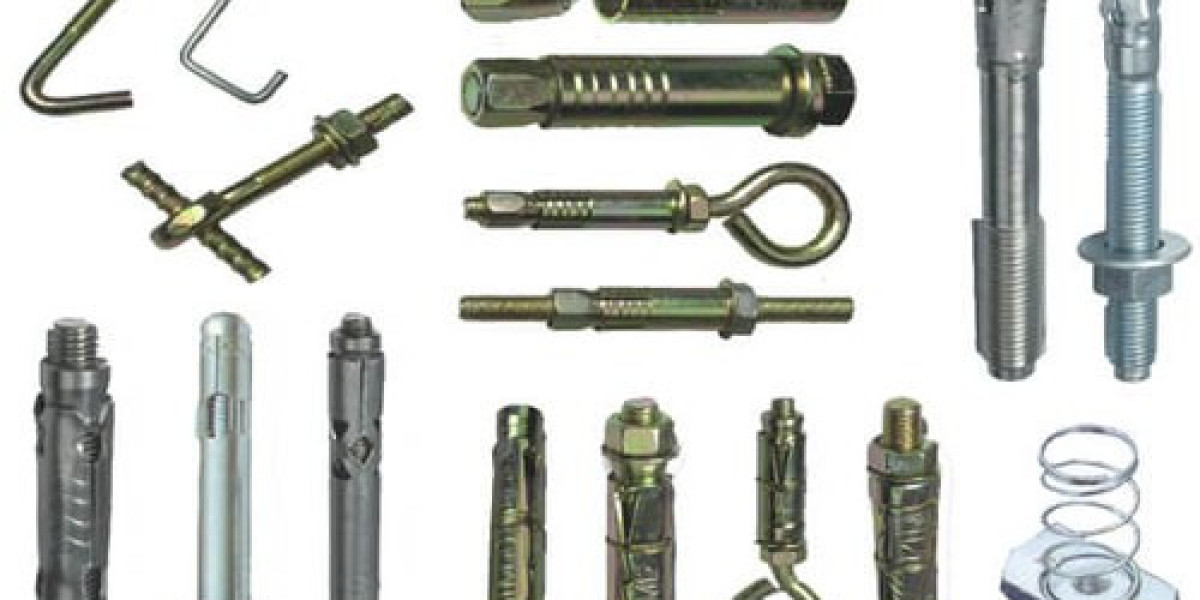
Fasteners are essential components in construction, manufacturing, and everyday DIY projects. They help in joining two or more objects together, providing stability and durability to structures and products. With a wide variety of fasteners available, selecting the right one is crucial for ensuring the strength and integrity of an assembly. In this article, we will explore different types of fasteners, their uses, and how they function.
1. Screws
Screws are one of the most commonly used fasteners. They have a helical ridge, known as a thread, that enables them to hold materials together securely. Screws are available in various sizes, materials, and head types. Some common types of screws include:
a) Wood Screws
Designed for woodworking applications, wood screws have coarse threads and a sharp tip that helps them grip into wooden surfaces effectively.
b) Machine Screws
Machine screws are used in metal-to-metal or metal-to-plastic applications and often require a nut or tapped hole for secure fastening.
c) Self-Tapping Screws
These screws can cut their own threads into materials like metal or plastic, eliminating the need for pre-drilled holes.
d) Drywall Screws
Drywall screws are designed for fastening drywall to wooden or metal studs. They typically have a bugle head and fine or coarse threads.
e) Sheet Metal Screws
Used for attaching sheet metal, these screws have sharp threads that enable secure fastening in thin materials.
2. Bolts
Bolts are another popular fastener type that requires a nut to secure components together. They are commonly used in heavy-duty applications such as automotive, construction, and machinery. Types of bolts include:
a) Hex Bolts
Hex bolts, also known as hex cap screws, have a six-sided head and are commonly used in construction and machinery applications.
b) Carriage Bolts
These bolts have a smooth, rounded head with a square neck, preventing rotation when tightened.
c) Eye Bolts
Eye bolts have a looped head, allowing them to be used for lifting or attaching cables and ropes.
d) U-Bolts
U-bolts are shaped like a "U" and are primarily used for securing pipes or tubing to surfaces.
e) Anchor Bolts
Anchor bolts are used to attach objects to concrete structures, providing strong and durable fastening.
3. Nuts
Nuts are used in conjunction with bolts to secure components together. They come in different shapes and sizes to meet various requirements.
a) Hex Nuts
Hex nuts are six-sided and are the most commonly used type of nut.
b) Lock Nuts
Lock nuts have a special design that prevents loosening due to vibrations.
c) Wing Nuts
Wing nuts have two flat projections, allowing for manual tightening and loosening without tools.
d) Flange Nuts
Flange nuts have an integrated washer-like base, which distributes pressure and prevents damage to surfaces.
e) Cap Nuts
Cap nuts have a domed top, providing a finished appearance and protecting the bolt threads from damage.
4. Washers
Washers are flat, disk-shaped components used to distribute load and prevent damage to surfaces.
a) Flat Washers
These are the most common type, providing load distribution and reducing surface wear.
b) Lock Washers
Lock washers prevent nuts and bolts from loosening due to vibrations.
c) Fender Washers
Fender washers have a larger diameter, offering increased load distribution.
d) Split Washers
Split washers have a helical shape that exerts pressure on the nut and bolt to prevent loosening.
5. Rivets
Rivets are permanent fasteners used to join materials such as metal, plastic, and leather. Common types include:
a) Blind Rivets
Also known as pop rivets, these are used when access to only one side of the material is available.
b) Solid Rivets
Solid rivets are hammered into place and provide a strong, permanent joint.
c) Tubular Rivets
These have a hollow shaft, making them suitable for lightweight applications.
d) Split Rivets
Split rivets have legs that bend outward for a secure hold in soft materials like leather or plastic.
6. Anchors
Anchors are used to provide secure fastening in materials like concrete, brick, or drywall.
a) Expansion Anchors
These expand within the hole to provide a strong grip.
b) Toggle Bolts
Toggle bolts have wings that expand behind the surface for a secure hold in hollow materials.
c) Sleeve Anchors
Sleeve anchors expand within the hole to create a strong hold in masonry materials.
d) Plastic Anchors
Plastic anchors are lightweight and used for securing screws in drywall or masonry.
7. Pins
Pins are non-threaded fasteners used for positioning, aligning, or securing components.
a) Dowel Pins
Dowel pins are cylindrical rods used for precise alignment in machinery and furniture.
b) Cotter Pins
Cotter pins are bent metal pins used to secure nuts and bolts in place.
c) Roll Pins
Roll pins are slotted cylindrical pins used to secure components under high pressure.
Conclusion
Fasteners play a crucial role in various industries and everyday applications. Choosing the right fastener depends on factors such as material, load requirements, and environmental conditions. Understanding the different types of fasteners and their uses will help ensure strong and reliable connections in any project.